借助 CSS Anchor Positioning API,您可以相对于其他元素(称为锚点)定位元素。此 API 简化了许多界面功能(例如菜单和子菜单、提示、选择器、标签、卡片、设置对话框等)的复杂布局要求。借助内置于浏览器中的锚点定位,您无需依赖第三方库即可构建分层界面,从而开启无限的创意可能性。
核心概念:锚点和定位元素
此 API 的核心在于锚点与定位元素之间的关系。锚点是使用 anchor-name 属性指定为参考点的元素。定位元素是指使用 position-anchor 属性或在定位逻辑中明确使用 anchor-name 相对于锚点放置的元素。

设置锚点
创建锚点非常简单。将 anchor-name 属性应用于所选元素,并为其分配一个唯一标识符。此唯一标识符必须以双短划线开头,就像 CSS 变量一样。
.anchor-button {
anchor-name: --anchor-el;
}
分配锚点名称后,.anchor-button 就会用作锚点,以便引导其他元素的放置。您可以通过以下两种方式之一将此锚点连接到其他元素:
隐式锚点
将锚点连接到其他元素的第一种方法是使用隐式锚点,如以下代码示例所示。position-anchor 属性会添加到您要连接到锚点的元素中,并将锚点的名称(在本例中为 --anchor-el)作为值。
.positioned-notice {
position-anchor: --anchor-el;
}
使用隐式锚点关系时,您可以使用 anchor() 函数来定位元素,而无需在其第一个参数中明确指定锚点名称。
.positioned-notice {
position-anchor: --anchor-el;
top: anchor(bottom);
}
显式锚点
或者,您也可以直接在锚点函数(例如 top: anchor(--anchor-el bottom)中使用锚点名称。这称为显式锚点,如果您想将视图锚定到多个元素,则非常有用(请继续阅读以查看示例)。
.positioned-notice {
top: anchor(--anchor-el bottom);
}
相对于锚点定位元素
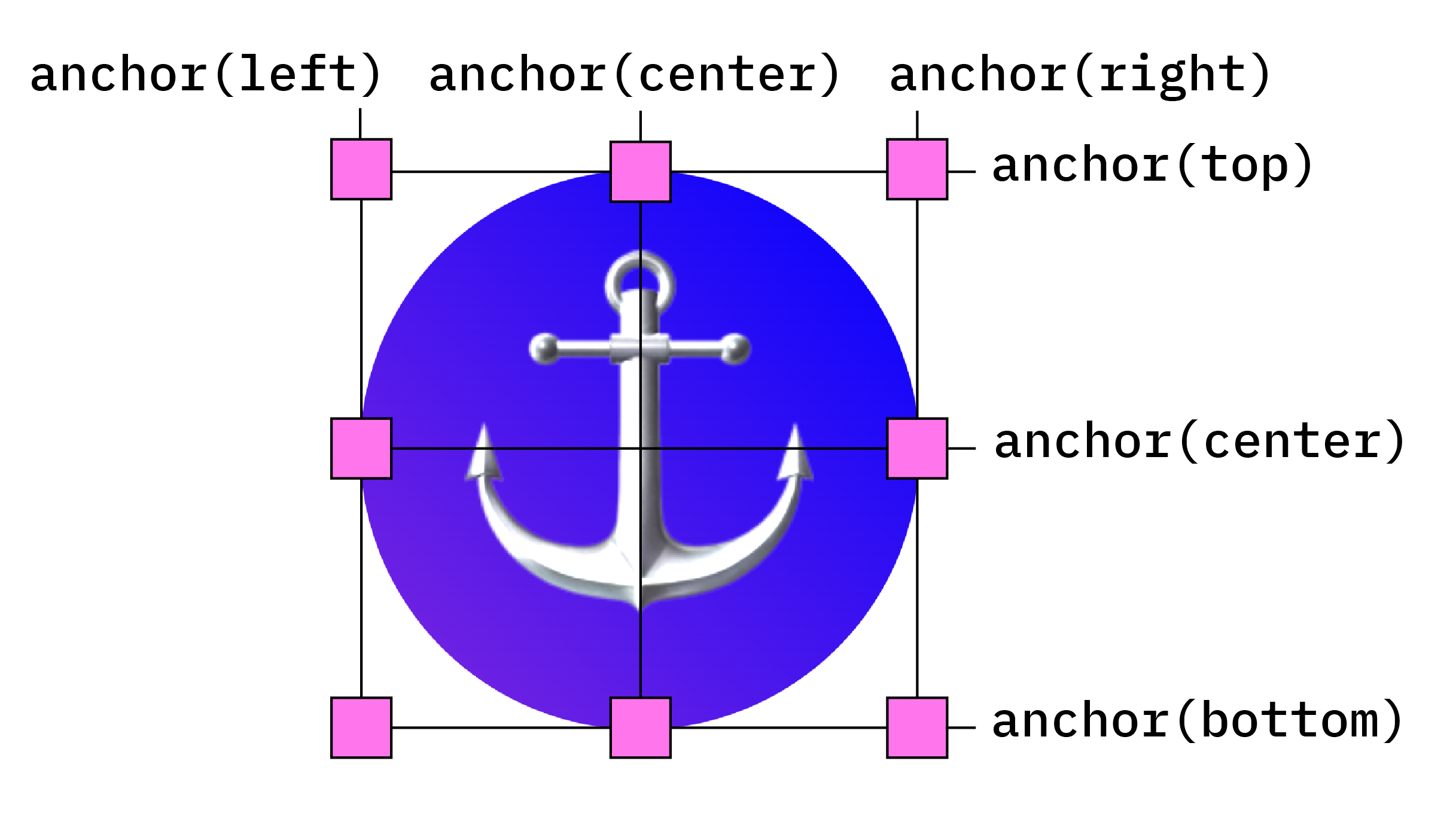
锚点定位基于 CSS 绝对定位。如需使用定位值,您需要向定位的元素添加 position: absolute。然后,使用 anchor() 函数应用定位值。例如,如需将锚定元素放置在锚定元素的左上角,请使用以下定位:
.positioned-notice {
position-anchor: --anchor-el;
/* absolutely position the positioned element */
position: absolute;
/* position the right of the positioned element at the right edge of the anchor */
right: anchor(right);
/* position the bottom of the positioned element at the top edge of the anchor */
bottom: anchor(top);
}
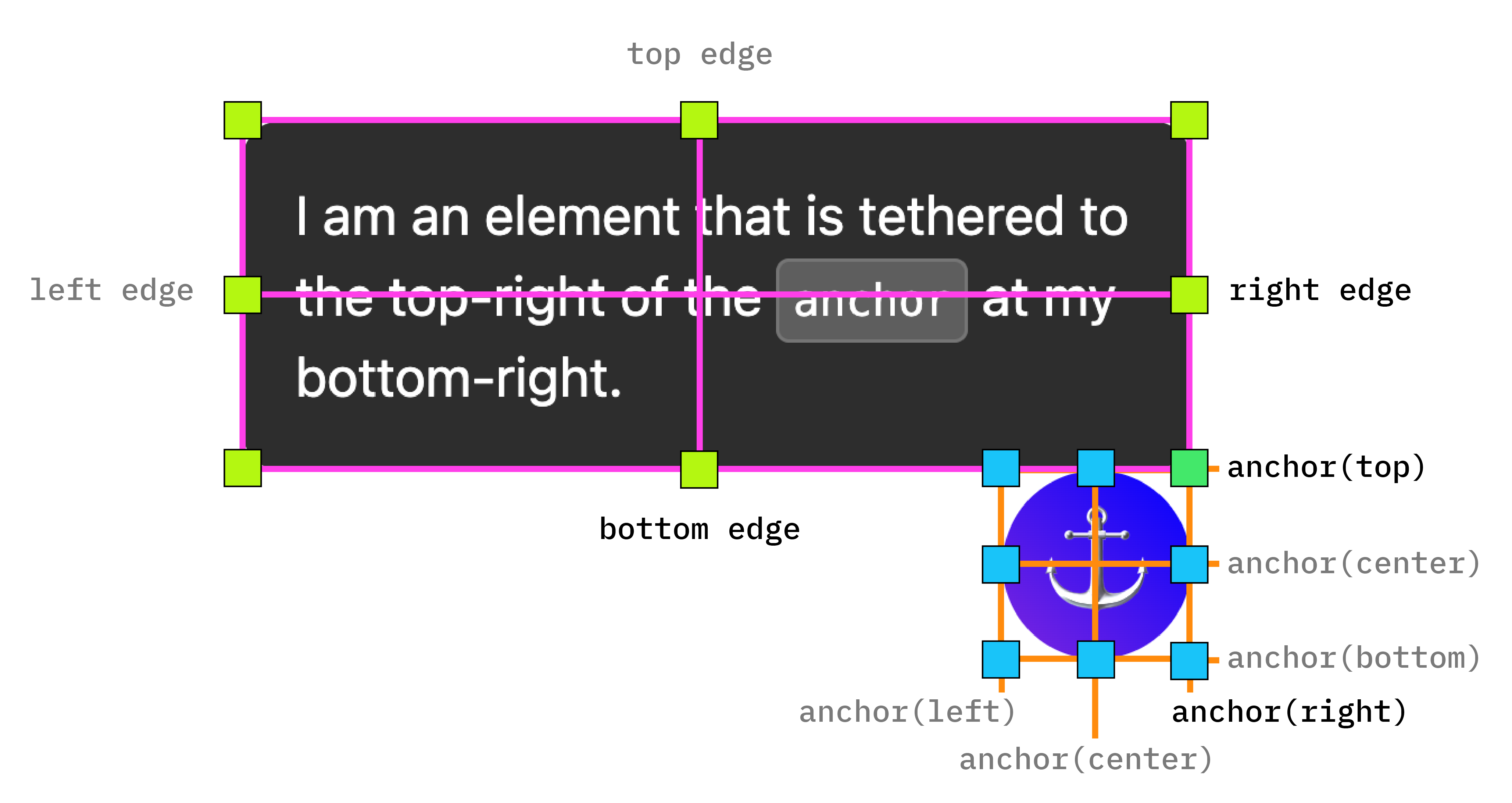
现在,一个元素已锚定到另一个元素,如下所示:

如需对这些值使用逻辑定位,请使用以下等效项:
top=inset-block-startleft=inset-inline-startbottom=inset-block-endright=inset-inline-end
使用 anchor-center 将定位元素居中
为了更轻松地将锚点定位的元素相对于其锚点居中,我们引入了一个名为 anchor-center 的新值,可与 justify-self、align-self、justify-items 和 align-items 属性搭配使用。
此示例通过使用 justify-self: anchor-center 将定位元素居中放置在其锚点上方来修改了前面的示例。
.positioned-notice {
position: absolute;
/* Anchor reference */
position-anchor: --anchor-el;
/* Position bottom of positioned elem at top of anchor */
bottom: anchor(top);
/* Center justification to the anchor */
justify-self: anchor-center;
}
justify-center 居中显示锚点的演示。
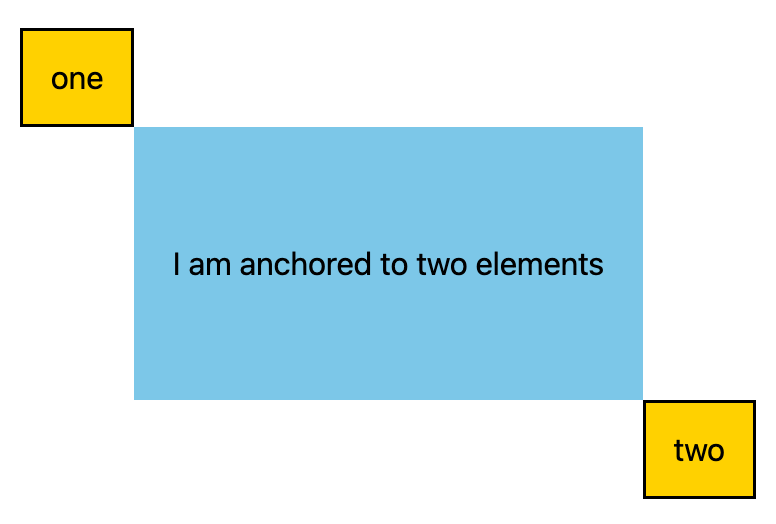
多个锚点
元素可以锚定到多个锚点。这意味着,您可能需要设置相对于多个锚点的位置值。为此,请使用 anchor() 函数,并在第一个参数中明确说明您引用的是哪个锚点。在以下示例中,定位元素的左上角锚定到一个锚点的右下角,而定位元素的右下角锚定到第二个锚点的左上角:
.anchored {
position: absolute;
top: anchor(--one bottom);
left: anchor(--one right);
right: anchor(--two left);
bottom: anchor(--two top);
}
使用 position-area 设置位置
锚点 API 包含使用 position-area 属性的新布局机制。
借助此属性,您可以相对于各自的锚点放置锚定定位的元素,并且适用于以锚定元素为中心的 9 个单元格的网格。
如需使用 position-area(而非绝对定位),请使用 position-area 属性,并附上物理值或逻辑值。例如:
- 顶部居中:
position-area: top或position-area: block-start - 左对齐:
position-area: left或position-area: inline-start - 底部居中:
position-area: bottom或position-area: block-end - 右对齐:
position-area: right或position-area: inline-end

如需进一步了解这些位置,请查看以下工具:
使用 anchor-size() 调整元素大小
anchor-size() 函数也属于锚点定位 API,可用于根据锚点的尺寸(宽度、高度或内嵌和块级尺寸)调整锚点定位元素的尺寸或位置。
以下 CSS 展示了将此属性用于高度的示例,其中在 calc() 函数中使用 anchor-size(height) 将提示的最大高度设置为锚点高度的两倍。
.positioned-notice {
position-anchor: --question-mark;
/* set max height of the tooltip to 2x height of the anchor */
max-height: calc(anchor-size(height) * 2);
}
anchor-size 演示
将锚点与弹出式窗口和对话框等顶层元素搭配使用
锚点定位非常适用于 popover 等顶层元素。和 <dialog>。虽然这些元素会放置在与 DOM 子树的其余部分分隔的单独层中,但借助锚点定位,您可以将这些元素重新绑定到顶层以外的元素,并与这些元素一起滚动。这对分层界面来说是一个巨大的胜利。
在以下示例中,使用按钮触发了一组提示信息弹出式窗口。按钮是锚点,而提示是定位元素。您可以像设置任何其他锚定元素一样设置定位元素的样式。在本示例中,anchor-name 和 position-anchor 是按钮和提示的内嵌样式。由于每个锚点都需要具有唯一性的锚点名称,因此在生成动态内容时,内嵌是最简单的方法。
popover 的锚点演示
使用 @position-try 调整锚点位置
确定初始锚点位置后,如果锚点到达其容器块的边缘,您可能需要调整位置。如需创建其他锚点位置,您可以将 @position-try 指令与 position-try-fallbacks 属性结合使用。
在以下示例中,子菜单显示在菜单的右侧。菜单和子菜单非常适合与锚点定位 API 和弹出式窗口属性搭配使用,因为这些菜单通常会锚定到触发器按钮。
对于此子菜单,如果横向空间不足,您可以将其移至菜单下方。为此,请先设置初始位置:
#submenu {
position: absolute;
position-anchor: --submenu;
/* initial position */
margin-left: var(--padding);
position-area: right span-bottom;
}
然后,使用 @position-try 设置回退锚定位置:
/* alternate position */
@position-try --bottom {
margin: var(--padding) 0 0 var(--padding);
posotion-area: bottom;
}
最后,使用 position-try-fallbacks 将这两个类连接起来。所有代码加起来,如下所示:
#submenu {
position: absolute;
position-anchor: --submenu;
/* initial position */
margin-left: var(--padding);
position-area: right span-bottom;
*/ connect with position-try-fallbacks */
position-try-fallbacks: --bottom;
}
/* alternate position */
@position-try --bottom {
margin: var(--padding) 0 0 var(--padding);
position-area: bottom;
}
popover 的锚点的演示锚点位置自动翻转关键字
如果您要进行基本调整(例如从上到下或从左到右翻转,或同时进行这两种翻转),甚至可以跳过创建自定义 @position-try 声明的步骤,并使用浏览器支持的内置翻转关键字(例如 flip-block 和 flip-inline)。这些替代项可用作自定义 @position-try 声明,并且可以相互结合使用:
position-try-fallbacks: flip-block, flip-inline, flip-block flip-inline;
翻转关键字可以显著简化您的锚点代码。只需几行代码,您就可以创建具有替代位置的完全功能的锚点:
#my-tooltip {
position-anchor: --question-mark;
position-area: top;
position-try-fallbacks: flip-block;
}
position-try-fallbacks: flip-block 自动翻转子滚动条中的锚点的 position-visibility
在某些情况下,您可能希望将某个元素锚定在网页的子滚动条中。在这些情况下,您可以使用 position-visibility 控制锚点的可见性。锚点何时会保持在视野中?此图标何时会消失?借助此功能,您可以控制这些选项。如果您希望定位的元素在锚点离开视野之前保持在视野中,请使用 position-visibility: anchors-visible:
#tooltip {
position: fixed;
position-anchor: --anchor-top-anchor;
position-visibility: anchors-visible;
bottom: anchor(top);
}
position-visibility: anchors-visible 演示或者,您也可以使用 position-visibility: no-overflow 来防止锚点溢出其容器。
#tooltip {
position: absolute;
position-anchor: --anchor-top-anchor;
position-visibility: no-overflow;
bottom: anchor(top);
}
position-visibility: no-overflow 演示功能检测和 polyfill
由于目前浏览器支持有限,因此您可能需要在使用此 API 时采取一些预防措施。首先,您可以使用 @supports 功能查询直接在 CSS 中检查是否受支持。为此,请将您的锚点样式封装在以下代码中:
@supports (anchor-name: --myanchor) {
/* Anchor styles here */
}
此外,您还可以使用 Oddbird 的 CSS 锚点定位 polyfill 对锚点定位功能进行 polyfill,该 polyfill 适用于 Firefox 54、Chrome 51、Edge 79 和 Safari 10。此 polyfill 支持大多数基本锚点位置功能,但当前实现尚不完整,并且包含一些过时的语法。您可以使用 unpkg 链接,也可以直接在软件包管理器中导入该文件。
关于无障碍功能的说明
虽然锚点定位 API 允许将元素相对于其他元素进行定位,但它本身不会在这些元素之间建立任何有意义的语义关系。如果锚点元素与定位元素之间实际上存在语义关系(例如,定位元素是关于锚点文本的边栏注释),则可以使用 aria-details 从锚点元素指向定位元素。屏幕阅读器软件仍在学习如何处理 aria-details,但支持功能正在不断改进。
<div class="anchor" aria-details="sidebar-comment">Main content</div>
<div class="positioned" id="sidebar-comment">Sidebar content</div>
.anchor {
anchor-name: --anchor;
}
.positioned {
position: fixed;
position-anchor: --anchor;
}
如果您将锚点定位与 popover 属性或 <dialog> 元素搭配使用,浏览器会处理焦点导航更正,以实现适当的无障碍功能,因此您无需按 DOM 顺序排列弹出式窗口或对话框。如需了解详情,请参阅规范中的无障碍注意事项。


