When using Trusted Web Activity in their applications, developers may need to pass information from the native part of the application into the Progressive Web App (PWA).
A common use-case for this is implementing custom analytics segmentations to measure installations and sessions started from the Trusted Web Activity. Query parameters can be added to the launch URL to implement this.
Modifying the start URL
If the parameter being passed to the PWA will remain the same across users and launches, the parameter can be appended directly to the launch URL. An example of this usage is when developers want to measure the number of navigation sessions created from a Trusted Web Activity.
Using Bubblewrap
Bubblewrap is a tool created to help developers to creating a Project for an Android application that launches an existing PWAs using a Trusted Web Activity. It contains both a library and a Command Line Interface (CLI).
Creating a new project
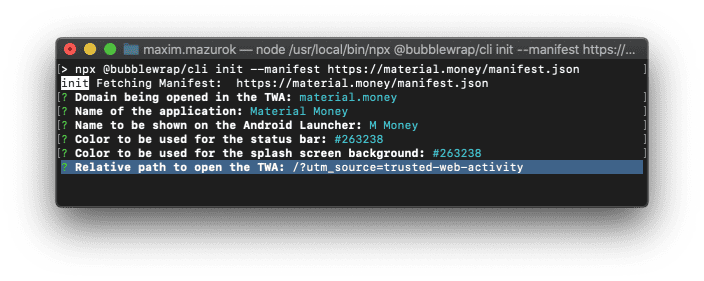
When using the Bubblewrap CLI, a project is initialized with the init command, and creates
default values from a Web Manifest, provided as a parameter:
bubblewrap init --manifest https://material.money/manifest.json
The wizard will use the start_url from the Web Manifest as default and will ask users to confirm the value, giving developers the chance to add extra parameters to the url used to start the Progressive Web App.
Modifying an existing project
When Bubblewrap generates a project, information for that particular project is stored in a file
called twa-manifest.json, in the project folder. To modify the start url for existing project,
developers need to modify the file:
{
...
"startUrl": "/?utm_source=trusted-web-activity",
...
}
Then, re-generate the project files and apply the new start URL
bubblewrap update
Using Android Studio
When using Android Studio and the default LauncherActivity, the startUrl is defined as a meta tag inside AndroidManifest.xml, and we can change the URL used to launch the Trusted Web Activity by modifying it:
<activity android:name="com.google.androidbrowserhelper.trusted.LauncherActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
...
<meta-data android:name="android.support.customtabs.trusted.DEFAULT_URL"
android:value="https://svgomg.firebaseapp.com/?utm_source=trusted-web-activity" />
...
</activity>
Modifying the start URL dynamically
In other cases, developers may want to create parameters that change across users or sessions, for instance. In most cases, this will involve collecting details from the Android side of the application to pass it to the Progressive Web App.
Step 1: Create a custom LauncherActivity
public class CustomQueryStringLauncherActivity extends LauncherActivity {
private String getDynamicParameterValue() {
return String.valueOf((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
}
@Override
protected Uri getLaunchingUrl() {
// Get the original launch Url.
Uri uri = super.getLaunchingUrl();
// Get the value we want to use for the parameter value
String customParameterValue = getDynamicParameterValue();
// Append the extra parameter to the launch Url
return uri
.buildUpon()
.appendQueryParameter("my_parameter", customParameterValue)
.build();
}
}
Step 2: Modify the AndroidManifest.xml to use the custom LauncherActivity
<activity android:name="com.myapp.CustomQueryStringLauncherActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
...
<meta-data android:name="android.support.customtabs.trusted.DEFAULT_URL"
android:value="https://squoosh.app/?utm_source=trusted-web-activity" />
...
</activity>
Conclusion
Passing information from the native part to the web part of an application can be achieved by using query parameters. When a parameter is added to the query string, it will be accessible to scripts running on the page and may also be part of the referral when users navigate to a different page or the developer implements a share action.
Developers must be aware of those implications, and can mitigate them using link rel=noreferrer or cleaning-up the URL using the page location API.
The Trusted Web Activity protocol doesn't currently provide a mechanism to exchange messages with the native part of the application after the web part is invoked.
We believe existing or upcoming Web Platform APIs enable most use cases needed by developers. If you are looking for new or upcoming Web APIs, check out the New Capabilities status page.

