इस चरण में आपको यह जानकारी मिलेगी:
- किसी मौजूदा वेब ऐप्लिकेशन को Chrome Apps प्लैटफ़ॉर्म के मुताबिक बनाने का तरीका.
- अपने ऐप्लिकेशन स्क्रिप्ट को कॉन्टेंट की सुरक्षा के बारे में नीति (सीएसपी) के मुताबिक बनाने का तरीका.
- chrome.storage.local का इस्तेमाल करके लोकल स्टोरेज लागू करने का तरीका.
इस चरण को पूरा करने में लगने वाला अनुमानित समय: 20 मिनट.
अभी तक किसी भी व्यक्ति ने चेक इन नहीं किया है
इस चरण में जो कुछ भी पूरा किया जाएगा उसकी झलक देखने के लिए, इस पेज पर सबसे नीचे जाएं ↓.
मौजूदा काम की सूची वाला ऐप्लिकेशन इंपोर्ट करें
शुरुआत में, TodoMVC का वेनिला JavaScript वर्शन इंपोर्ट करें. यह एक सामान्य मानदंड है आपके प्रोजेक्ट में जोड़ा जा सकता है.
हमने todomvc के रेफ़रंस कोड पिन में TodoMVC ऐप्लिकेशन का एक वर्शन शामिल किया है फ़ोल्डर खोलें. todomvc की सभी फ़ाइलों (फ़ोल्डर सहित) को अपने प्रोजेक्ट फ़ोल्डर में कॉपी करें.

आपसे index.html को बदलने के लिए कहा जाएगा. आगे बढ़ें और न्योता स्वीकार करें.

अब आपके ऐप्लिकेशन फ़ोल्डर में यह फ़ाइल संरचना होनी चाहिए:

नीले रंग से हाइलाइट की गई फ़ाइलें, todomvc फ़ोल्डर से ली गई हैं.
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को अब फिर से लोड करें (राइट-क्लिक करें > ऐप्लिकेशन को फिर से लोड करें). आपको बेसिक यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) दिखना चाहिए, लेकिन आप यह नहीं करेंगे आप काम की सूची जोड़ सकते हैं.
स्क्रिप्ट को कॉन्टेंट की सुरक्षा के बारे में नीति (सीएसपी) के मुताबिक बनाएं
DevTools कंसोल खोलें (राइट क्लिक करें > एलिमेंट की जांच करें, फिर कंसोल टैब चुनें). आपने लोगों तक पहुंचाया मुफ़्त में इनलाइन स्क्रिप्ट चलाने से मना करने के बारे में एक गड़बड़ी दिखेगी:
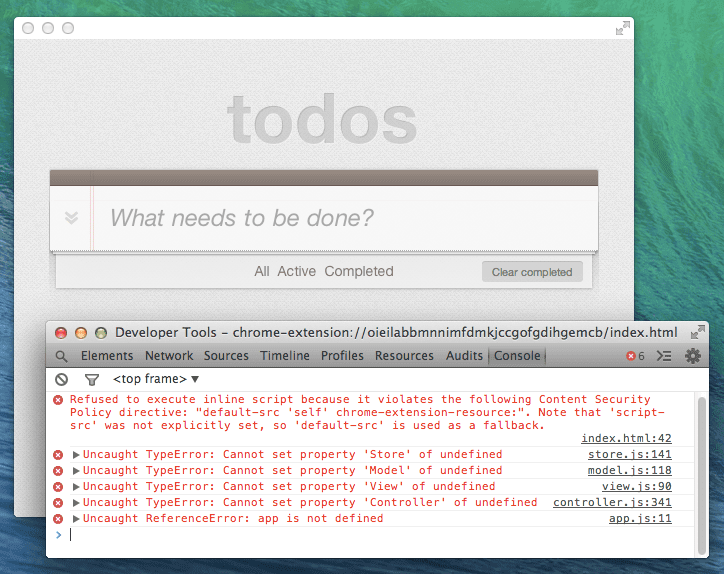
आइए, ऐप्लिकेशन को कॉन्टेंट की सुरक्षा के बारे में नीति के मुताबिक बनाकर इस गड़बड़ी को ठीक करते हैं. सबसे ज़्यादा
आम तौर पर, सीएसपी का पालन न करने की समस्या इनलाइन JavaScript की वजह से होती है. इनलाइन JavaScript के उदाहरणों में ये शामिल हैं
डीओएम एट्रिब्यूट (जैसे, <button onclick=''>) और कॉन्टेंट वाले <script> टैग के तौर पर इवेंट हैंडलर
एचटीएमएल में मौजूद है.
इसे हल करना आसान है: इनलाइन कॉन्टेंट को नई फ़ाइल में ले जाएं.
1. index.html के नीचे की ओर, इनलाइन JavaScript हटाएं और उसके बजाय js/bootstrap.js:
<script src="bower_components/director/build/director.js"></script>
<script>
// Bootstrap app data
window.app = {};
</script>
<script src="js/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="js/helpers.js"></script>
<script src="js/store.js"></script>
2. js फ़ोल्डर में bootstrap.js नाम की फ़ाइल बनाएं. पहले के इनलाइन कोड को एक जगह से दूसरी जगह ले जाएं इस फ़ाइल में होने के लिए:
// Bootstrap app data
window.app = {};
अगर आप अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को फिर से लोड करते हैं और आप उसके करीब हैं, तो आपके पास एक काम नहीं करने वाला Todo ऐप्लिकेशन होगा.
localStorage को chrome.storage.local में बदलें
DevTools कंसोल को अभी खोलने पर, पिछली गड़बड़ी हट जाएगी. एक नई गड़बड़ी हुई,
हालांकि, करीब window.localStorage उपलब्ध नहीं है:

Chrome ऐप्स localStorage का समर्थन नहीं करते, क्योंकि localStorage सिंक्रोनस है. सिंक्रोनस ऐक्सेस
अगर एक ही थ्रेड वाले रनटाइम में संसाधनों (I/O) को ब्लॉक किया जाता है, तो हो सकता है कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन काम न करे.
Chrome ऐप्स में एक समान एपीआई होता है जो ऑब्जेक्ट को एसिंक्रोनस रूप से स्टोर कर सकता है. इससे लोग, ऑब्जेक्ट->स्ट्रिंग->ऑब्जेक्ट को क्रम में लगाने की प्रोसेस बहुत ज़्यादा खर्ची होती है.
हमारे ऐप्लिकेशन में गड़बड़ी के मैसेज को ठीक करने के लिए, आपको localStorage को
chrome.storage.local.
ऐप्लिकेशन अनुमतियां अपडेट करें
chrome.storage.local का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, आपको storage की अनुमति का अनुरोध करना होगा. तय सीमा में
manifest.json में, permissions कलेक्शन में "storage" जोड़ें:
"permissions": ["storage"],
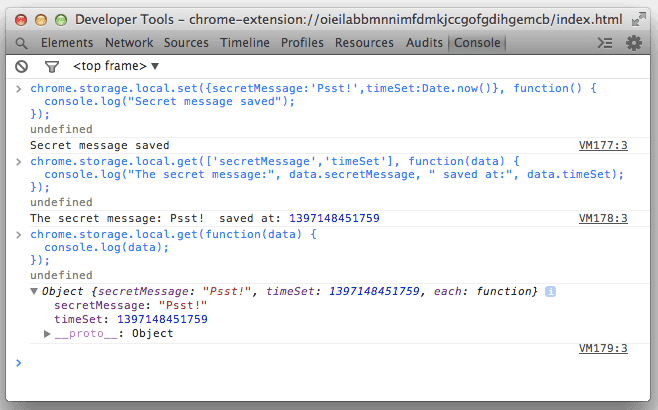
local.storage.set() और local.storage.get() के बारे में जानें
काम की सूची वाले आइटम सेव करने और वापस पाने के लिए, आपकोset()get()
chrome.storage एपीआई.
set() तरीका, पहले पैरामीटर के तौर पर की-वैल्यू पेयर के ऑब्जेक्ट को स्वीकार करता है. एक वैकल्पिक कॉलबैक फ़ंक्शन दूसरा पैरामीटर है. उदाहरण के लिए:
chrome.storage.local.set({secretMessage:'Psst!',timeSet:Date.now()}, function() {
console.log("Secret message saved");
});
get() तरीके से आपकी पसंद के डेटास्टोर कुंजियों के लिए एक वैकल्पिक पहला पैरामीटर स्वीकार किया जाता है वापस लाना. एक कुंजी को स्ट्रिंग के रूप में पास किया जा सकता है; कई कुंजियों को स्ट्रिंग या डिक्शनरी ऑब्जेक्ट.
दूसरा ज़रूरी पैरामीटर, कॉलबैक फ़ंक्शन है. लौटाए गए ऑब्जेक्ट में, सेव की गई वैल्यू को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए, पहले पैरामीटर में अनुरोध की गई कुंजियां. उदाहरण के लिए:
chrome.storage.local.get(['secretMessage','timeSet'], function(data) {
console.log("The secret message:", data.secretMessage, "saved at:", data.timeSet);
});
अगर आपको chrome.storage.local में मौजूद सारी जानकारी get() करनी है, तो पहले वाली शर्त को छोड़ दें
पैरामीटर:
chrome.storage.local.get(function(data) {
console.log(data);
});
localStorage के उलट, DevTools का इस्तेमाल करके डिवाइस में सेव किए गए आइटम की जांच नहीं की जा सकती
संसाधनों का पैनल. हालांकि, आप इस तरह के JavaScript कंसोल से chrome.storage के साथ इंटरैक्ट कर सकते हैं
इसलिए:
ज़रूरी एपीआई बदलावों की झलक देखें
Todo ऐप्लिकेशन को बदलने के लिए बाकी के ज़्यादातर चरण, एपीआई कॉल में किए गए छोटे-छोटे बदलाव हैं. बदला जा रहा है
उन सभी जगहों पर जहां फ़िलहाल localStorage का इस्तेमाल हो रहा है. हालांकि, इसमें ज़्यादा समय लगता है और गड़बड़ी होने की संभावना भी ज़्यादा होती है,
आवश्यक है.
localStorage और chrome.storage के बीच के मुख्य अंतर, एक साथ काम न करने वाली सेटिंग की वजह से हैं
chrome.storage:
सामान्य असाइनमेंट का इस्तेमाल करके
localStorageको लिखने के बजाय, आपको वैकल्पिक कॉलबैक के साथchrome.storage.local.set().var data = { todos: [] }; localStorage[dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);बनाम
var storage = {}; storage[dbName] = { todos: [] }; chrome.storage.local.set( storage, function() { // optional callback });localStorage[myStorageName]को सीधे ऐक्सेस करने के बजाय, आपकोchrome.storage.local.get(myStorageName,function(storage){...})और फिर लौटाए गए सामान को पार्स करना होगा कॉलबैक फ़ंक्शन मेंstorageऑब्जेक्ट है.var todos = JSON.parse(localStorage[dbName]).todos;बनाम
chrome.storage.local.get(dbName, function(storage) { var todos = storage[dbName].todos; });.bind(this)फ़ंक्शन का इस्तेमाल सभी कॉलबैक पर किया जाता है, ताकि यह पक्का किया जा सके किthisthisStoreप्रोटोटाइप. (बाउंड फ़ंक्शन के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी MDN दस्तावेज़ों पर मिल सकती है: Function.prototype.bind().)function Store() { this.scope = 'inside Store'; chrome.storage.local.set( {}, function() { console.log(this.scope); // outputs: 'undefined' }); } new Store();बनाम
function Store() { this.scope = 'inside Store'; chrome.storage.local.set( {}, function() { console.log(this.scope); // outputs: 'inside Store' }.bind(this)); } new Store();
इन मुख्य अंतरों को ध्यान में रखें क्योंकि हम इसमें सेक्शन पढ़ें.
सूची में मौजूद आइटम वापस लाएं
काम की सूची वापस पाने के लिए, आइए काम की सूची वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को अपडेट करें:
1. Store कंस्ट्रक्टर वाला तरीका, Todo ऐप्लिकेशन को पहले से मौजूद सभी
डेटास्टोर से करने के लिए आइटम. इस तरीके से पहले यह पता चलता है कि डेटा स्टोर मौजूद है या नहीं. अगर ऐसा नहीं है, तो
todos का खाली अरे बनाएं और उसे डेटास्टोर में सेव करें, ताकि रनटाइम के दौरान पढ़ने वाली कोई गड़बड़ी न हो.
js/store.js में, कंस्ट्रक्टर में localStorage के इस्तेमाल को बदलें
chrome.storage.local:
function Store(name, callback) {
var data;
var dbName;
callback = callback || function () {};
dbName = this._dbName = name;
if (!localStorage[dbName]) {
data = {
todos: []
};
localStorage[dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);
}
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[dbName]));
chrome.storage.local.get(dbName, function(storage) {
if ( dbName in storage ) {
callback.call(this, storage[dbName].todos);
} else {
storage = {};
storage[dbName] = { todos: [] };
chrome.storage.local.set( storage, function() {
callback.call(this, storage[dbName].todos);
}.bind(this));
}
}.bind(this));
}
2. मॉडल से काम की सूची पढ़ते समय, find() तरीके का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. नतीजों में दिखने वाले नतीजे अलग-अलग होते हैं
"सभी", "चालू है" या "पूरा हो गया" के हिसाब से फ़िल्टर करना है.
chrome.storage.local का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए find() को बदलें:
Store.prototype.find = function (query, callback) {
if (!callback) {
return;
}
var todos = JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos;
callback.call(this, todos.filter(function (todo) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var todos = storage[this._dbName].todos.filter(function (todo) {
for (var q in query) {
return query[q] === todo[q];
}
});
callback.call(this, todos);
}.bind(this));
}));
};
3. find() के समान, findAll() को मॉडल से सभी काम की सूची मिलती है. findAll() को इस्तेमाल करने के लिए बदलें
chrome.storage.local:
Store.prototype.findAll = function (callback) {
callback = callback || function () {};
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos);
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var todos = storage[this._dbName] && storage[this._dbName].todos || [];
callback.call(this, todos);
}.bind(this));
};
काम की सूची सेव करें
save() का मौजूदा तरीका एक चैलेंज है. यह एक साथ काम नहीं करने वाली दो कार्रवाइयों पर निर्भर करता है (पाएं और सेट करें)
जो हर बार पूरे मोनोलिथिक JSON स्टोरेज पर काम करती हैं. एक से ज़्यादा बैच पर अपडेट होता है
काम की सूची, जैसे "सभी काम की सूची 'पूरा हो गया' के तौर पर मार्क करें", तो नतीजे के तौर पर डेटा से होने वाला खतरा
लिखने के बाद पढ़ना. अगर हम ज़्यादा सही डेटा स्टोरेज,
जैसे, IndexedDB, लेकिन हम इस कोडलैब के लिए कन्वर्ज़न प्रोसेस को कम करने की कोशिश कर रहे हैं.
इसे ठीक करने के कई तरीके हैं. इसलिए, हम इस मौके का इस्तेमाल करके, save() में थोड़ा बदलाव करेंगे
एक साथ अपडेट करने के लिए काम की सूची वाले आईडी का कलेक्शन बनाना:
1. शुरू करने के लिए, save() में पहले से मौजूद सभी चीज़ों को chrome.storage.local.get() की मदद से रैप करें
कॉलबैक:
Store.prototype.save = function (id, updateData, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]);
// ...
if (typeof id !== 'object') {
// ...
}else {
// ...
}
}.bind(this));
};
2. localStorage के सभी इंस्टेंस को chrome.storage.local की मदद से बदलें:
Store.prototype.save = function (id, updateData, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]);
var data = storage[this._dbName];
var todos = data.todos;
callback = callback || function () {};
// If an ID was actually given, find the item and update each property
if ( typeof id !== 'object' ) {
// ...
localStorage[this._dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos);
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
callback.call(this, storage[this._dbName].todos);
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
} else {
callback = updateData;
updateData = id;
// Generate an ID
updateData.id = new Date().getTime();
localStorage[this._dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);
callback.call(this, [updateData]);
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
callback.call(this, [updateData]);
}.bind(this));
}
}.bind(this));
};
3. इसके बाद, किसी एक आइटम के बजाय किसी कलेक्शन पर ऑपरेट करने के लिए, लॉजिक को अपडेट करें:
Store.prototype.save = function (id, updateData, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = storage[this._dbName];
var todos = data.todos;
callback = callback || function () {};
// If an ID was actually given, find the item and update each property
if ( typeof id !== 'object' || Array.isArray(id) ) {
var ids = [].concat( id );
ids.forEach(function(id) {
for (var i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id == id) {
for (var x in updateData) {
todos[i][x] = updateData[x];
}
}
}
});
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
callback.call(this, storage[this._dbName].todos);
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
} else {
callback = updateData;
updateData = id;
// Generate an ID
updateData.id = new Date().getTime();
todos.push(updateData);
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
callback.call(this, [updateData]);
}.bind(this));
}
}.bind(this));
};
ज़रूरी आइटम को 'पूरा हो गया' के तौर पर मार्क करें
अब जब ऐप्लिकेशन, कलेक्शन पर काम कर रहा है, तो आपको यह बदलना होगा कि ऐप्लिकेशन, पूरा हुआ (#) हटाएं बटन:
1. controller.js में, अरे के साथ toggleComplete() को सिर्फ़ एक बार कॉल करने के लिए, toggleAll() को अपडेट करें
टास्क को एक-एक करके 'पूरा हुआ' के तौर पर मार्क करने की ज़रूरत नहीं. _filter() को किया गया कॉल भी मिटाएं
क्योंकि आपको toggleComplete _filter() में बदलाव करना है.
Controller.prototype.toggleAll = function (e) {
var completed = e.target.checked ? 1 : 0;
var query = 0;
if (completed === 0) {
query = 1;
}
this.model.read({ completed: query }, function (data) {
var ids = [];
data.forEach(function (item) {
this.toggleComplete(item.id, e.target, true);
ids.push(item.id);
}.bind(this));
this.toggleComplete(ids, e.target, false);
}.bind(this));
this._filter();
};
2. अब एक या कई कामों की सूची, दोनों को स्वीकार करने के लिए, toggleComplete() को अपडेट करें. इसमें ये शामिल हैं
filter() को बाहर के बजाय, update() के अंदर ले जा रहा है.
Controller.prototype.toggleComplete = function (ids, checkbox, silent) {
var completed = checkbox.checked ? 1 : 0;
this.model.update(ids, { completed: completed }, function () {
if ( ids.constructor != Array ) {
ids = [ ids ];
}
ids.forEach( function(id) {
var listItem = $$('[data-id="' + id + '"]');
if (!listItem) {
return;
}
listItem.className = completed ? 'completed' : '';
// In case it was toggled from an event and not by clicking the checkbox
listItem.querySelector('input').checked = completed;
});
if (!silent) {
this._filter();
}
}.bind(this));
};
Count todo items
After switching to async storage, there is a minor bug that shows up when getting the number of todos. You'll need to wrap the count operation in a callback function:
1. In model.js, update getCount() to accept a callback:
Model.prototype.getCount = function (callback) {
var todos = {
active: 0,
completed: 0,
total: 0
};
this.storage.findAll(function (data) {
data.each(function (todo) {
if (todo.completed === 1) {
todos.completed++;
} else {
todos.active++;
}
todos.total++;
});
if (callback) callback(todos);
});
return todos;
};
2. Back in controller.js, update _updateCount() to use the async getCount() you edited in
the previous step:
Controller.prototype._updateCount = function () {
var todos = this.model.getCount();
this.model.getCount(function(todos) {
this.$todoItemCounter.innerHTML = this.view.itemCounter(todos.active);
this.$clearCompleted.innerHTML = this.view.clearCompletedButton(todos.completed);
this.$clearCompleted.style.display = todos.completed > 0 ? 'block' : 'none';
this.$toggleAll.checked = todos.completed === todos.total;
this._toggleFrame(todos);
}.bind(this));
};
You are almost there! If you reload the app now, you will be able to insert new todos without any console errors.
Remove todos items
Now that the app can save todo items, you're close to being done! You still get errors when you attempt to remove todo items:

1. In store.js, convert all the localStorage instances to use chrome.storage.local:
a) To start off, wrap everything already inside remove() with a get() callback:
Store.prototype.remove = function (id, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]);
var todos = data.todos;
for (var i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id == id) {
todos.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
localStorage[this._dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos);
}.bind(this));
};
b) Then convert the contents within the get() callback:
Store.prototype.remove = function (id, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]);
var data = storage[this._dbName];
var todos = data.todos;
for (var i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id == id) {
todos.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
localStorage[this._dbName] = JSON.stringify(data);
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos);
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
callback.call(this, todos);
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
};
2. The same Read-After-Write data hazard issue previously present in the save() method is also
present when removing items so you will need to update a few more places to allow for batch
operations on a list of todo IDs.
a) Still in store.js, update remove():
Store.prototype.remove = function (id, callback) {
chrome.storage.local.get(this._dbName, function(storage) {
var data = storage[this._dbName];
var todos = data.todos;
var ids = [].concat(id);
ids.forEach( function(id) {
for (var i = 0; i < todos.length; i++) {
if (todos[i].id == id) {
todos.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
});
chrome.storage.local.set(storage, function() {
callback.call(this, todos);
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
};
b) In controller.js, change removeCompletedItems() to make it call removeItem() on all IDs
at once:
Controller.prototype.removeCompletedItems = function () {
this.model.read({ completed: 1 }, function (data) {
var ids = [];
data.forEach(function (item) {
this.removeItem(item.id);
ids.push(item.id);
}.bind(this));
this.removeItem(ids);
}.bind(this));
this._filter();
};
c) Finally, still in controller.js, change the removeItem() to support removing multiple items
from the DOM at once, and move the _filter() call to be inside the callback:
Controller.prototype.removeItem = function (id) {
this.model.remove(id, function () {
var ids = [].concat(id);
ids.forEach( function(id) {
this.$todoList.removeChild($$('[data-id="' + id + '"]'));
}.bind(this));
this._filter();
}.bind(this));
this._filter();
};
काम की सूची वाले सभी आइटम छोड़ें
store.js में localStorage का इस्तेमाल करके, एक और तरीका है:
Store.prototype.drop = function (callback) {
localStorage[this._dbName] = JSON.stringify({todos: []});
callback.call(this, JSON.parse(localStorage[this._dbName]).todos);
};
मौजूदा ऐप्लिकेशन में इस तरीके को कॉल नहीं किया जा रहा है. इसलिए, अगर आपको अतिरिक्त चैलेंज चाहिए, तो
आप उसे कैसे लागू कर सकते हैं. संकेत: chrome.storage.local.clear() पर एक नज़र डालें.
अपना काम पूरा करने वाला काम पूरा करने वाला ऐप्लिकेशन लॉन्च करें
आपने दूसरा चरण पूरा कर लिया है! अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को फिर से लोड करें. अब आपके पास Chrome का पैकेज किया हुआ वर्शन होना चाहिए कंपनी है.
अधिक जानकारी के लिए
इस चरण में शुरू किए गए कुछ एपीआई के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, यह लेख पढ़ें:
- कॉन्टेंट की सुरक्षा के बारे में नीति ↑
- अनुमतियों का एलान करना ↑
- chrome.storage ↑
- chrome.storage.local.get() ↑
- chrome.storage.local.set() ↑
- chrome.storage.local.remove() ↑
- chrome.storage.local.clear() ↑
क्या आप अगले चरण पर जाने के लिए तैयार हैं? तीसरा चरण - अलार्म और सूचनाएं जोड़ें » पर जाएं

